Geological Time Scale
The geologic time scale is a chronological dating system that classifies geological strata in time. This time scale is used by geologists, Paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe timing, relationships, and other events related to our planet in geologic history.
- The geologic time scale is a calendar for events in Earth’s history.
- An Eon is the largest period of geological time.
- The subdivisions Eras are formed by the combination of periods, we can say eras are subdivided into periods.
- Epochs combine together to form periods.
- The epoch is the smallest unit of time scale.
Table: Geological Time Scale
The geological time scale depicting the evolution of life forms from unicellular bacteria to modern man is given below.
| Era | Period | Epoch | Age | Life/major events |
| Cainozoic (From 65 million years ago to present time) | Quaternary | Holocene
Pleistocene |
0-10,000
10,000 – 2 Million |
Modern Man
Homo Sapiens |
| Tertiary | Pliocene | 2-5 Million | Early Human Ancestor | |
| Miocene | 5-24 Million | Ape: Flowering Plants and Trees | ||
| Oligocene | 24-37 Million | Anthropoid Ape | ||
| Eocene | 37-58 Million | Rabbits and Hare | ||
| Palaeocene | 57-65 Million | Small Mammals: Rats-Mice | ||
| Mesozoic 65-245 Million Mammals | Cretaceous | 65-144 Million | Extinction of Dinosaurs | |
| Jurassic | 144-208 Million | Age of Dinosaurs | ||
| Triassic | 208-245 Million | Frog and turtles | ||
| Palaeozoic 245-570 Million | Permian | 245-286 Million | Reptile dominate-replace amphibians | |
| Carboniferous | 286-360 Million | First Reptiles: Vertebrates: Coal beds | ||
| Devonian | 360-408 Million | Amphibians | ||
| Silurian | 408-438 Million | The first trace of life on land: Plant | ||
| Ordovician | 438-505 Million | First Fish | ||
| Cambrian | 505-570 Million | No terrestrial life: Marine Invertebrate | ||
| Pre-Cambrian 570 Million -4,800 Million | 570-2,500 Million | Soft-bodied arthropods | ||
| 2,500-3,800 Million | Blue-green algae: Unicellular bacteria | |||
| 3,800-4,800 Million | Oceans and Continents form-Ocean and Atmosphere are rich in Carbon dioxide | |||
| 5,000 – 13,700 Million | 5,000- Million
12,000 Million 13,700 Million |
Origin of the universe
Origin of the Sun stars Supernova, Big Bang |
The image given below shows the geological time scale:
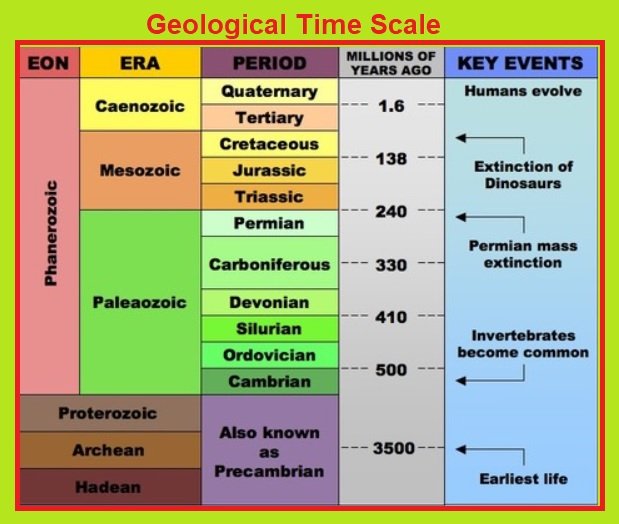
Origin of Life
The last phase in the evolution of the earth relates to the origin and evolution of life. Modern scientists refer to the origin of life as a kind of chemical reaction, which first generated complex organic molecules and assembled them. This assemblage that they could duplicate themselves by converting inanimate matter into living substances.
- The record of life that existed on this planet in different periods is found in rocks in the form of fossils.
- The microscopic structures closely related to the present form of blue algae have been found in geological formations much older than some 3,000 million years.
- It can be assumed that life began to evolve sometime 3,800 million years ago.
You can also read:
- The Solar System
- Atmosphere: Composition and Structure
- Volcanoes
- List of main volcanoes in the world
Thank you 🙂






[…] Click here to read: geological time scale (depicting the evolution of life from unicellular bacteria…. […]